
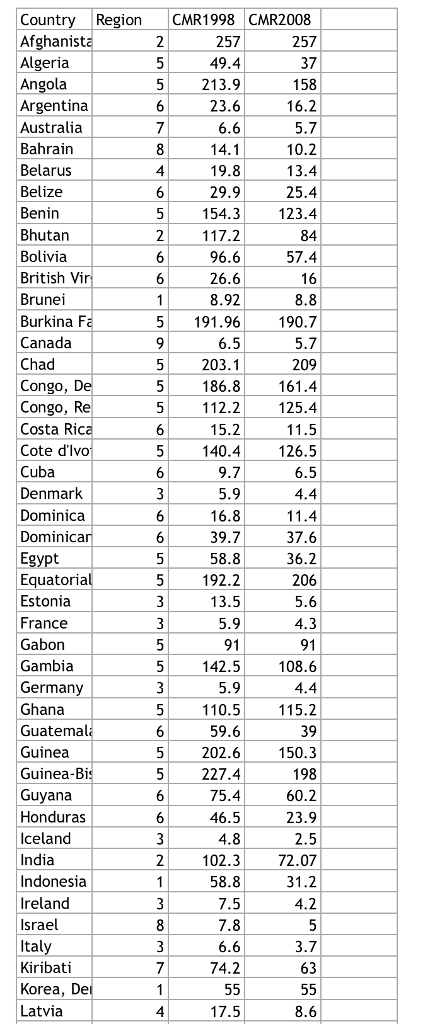
When working with a sample population, Bessel's correction can provide a better estimation of the standard deviation. It appears in formulas as n-1, where n is the count. However, when you calculate statistics for a sample, results are estimates and therefore not as accurate.īessel's correction is an adjustment made to correct for bias that occurs when working with sample data. When you calculate statistics for an entire population (mean, variance, etc.) results are accurate because all data is available. IF the data is just a sample, and you want to extrapolate to the entire population, you can use the STDEV.S function to correct for sample bias as explained below. If the data represents the entire population, you can use the STDEV.P function. To calculate standard deviation in Excel, you can use one of two primary functions, depending on the data set. However, please note that the student’s t-test is applicable for data set with a sample size of less than 30.Standard deviation is a measure of how much variance there is in a set of numbers compared to the average (mean) of the numbers. This test is run to check the validity of a null hypothesis based on the critical value at a given confidence interval and degree of freedom. It is imperative for a statistician to understand the concept of t-test as it holds significant importance while drawing conclusive evidence about whether or not two data sets have statistics that are not very different. T = ( x̄ 1 – x̄ 2) / √ Relevance and Use of t-Test Formula
Step 4: Finally, the formula for a two-sample t-test can be derived using observed sample means (step 1), sample standard deviations (step 2) and sample sizes (step 3) as shown below. Step 3: Next, determine the size of the two samples, which are denoted by and. Step 2: Next, determine the standard deviation of the two samples, which are denoted by and. Step 1: Firstly, determine the observed sample mean of the two samples under consideration. The formula for the two-sample t-test can be derived by using the following steps: Step 4: Finally, the formula for a one-sample t-test can be derived using the observed sample mean (step 1), the theoretical population means (step 1), sample standard deviation (step 2) and sample size (step 3), as shown below. Step 3: Next, determine the sample size, which is the number of data points in the sample. Step 2: Next, determine the standard deviation of the sample, and it is denoted by s. The sample mean and population mean is denoted by and μ, respectively.
/Excel-Variance-be33639762bf4b61b9bd6b321bb8277d.jpg)
Step 1: Firstly, determine the observed sample mean, and the theoretical population means specified.
The formula for one-sample t-test can be derived by using the following steps: So, the hypothesis that the statistics of the two samples are significantly different can’t be rejected. Therefore, the absolute t-test value is 4.31, which is greater than the critical value (3.03) at a 99.5% confidence interval with a degree of freedom of 30. T-Test value is calculated using the formula given below Determine if the sample’s statistics are different at a 99.5% confidence interval. The two samples have means of 10 and 12, standard deviations of 1.2 and 1.4, and sample sizes of 17 and 15. Let us take the example of two samples to illustrate the concept of a two-sample t-test.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
